Explain the factors involved in slant range.
If there is a relatively dense layer of haze or mist the runway may have better visibility from directly above, because the depth of penetration is better looking through at right angles
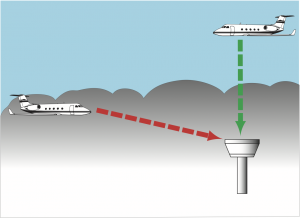
Explain the factors involved in slant range.
If there is a relatively dense layer of haze or mist the runway may have better visibility from directly above, because the depth of penetration is better looking through at right angles

Describe the operational problems associated with fog.

There are two sets of issues
1) Departure problems
– The fog can be easily misjudged based on an apparently thin layer but within a few kilometers worse or clearer conditions may exist
– Once having taken off through fog it is unlikely that a pilot would be able to land at the same airport
– A climb out in mountainous terrain will be affected by poor visibility
2) Arrival Problems
– on approach if the fog is developing, the slant range must be considered
– danger is involved when trying to land at the end of the day – in shadow the runway can be seen at right angles but on final approach the visibility distance may not be suffiicient
.png)
What are the terms used for describing the characteristics of cloud.
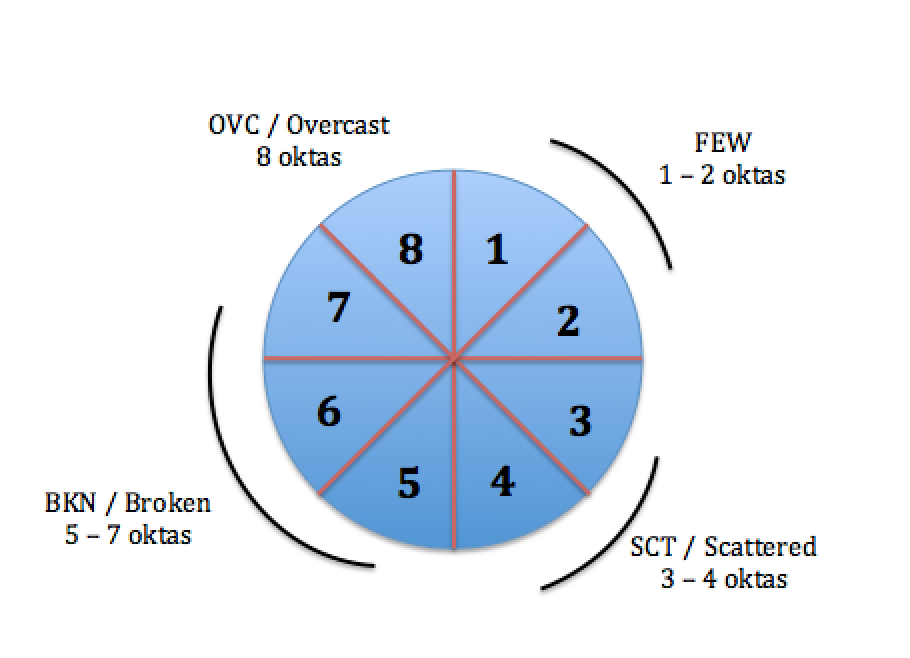
The main method for characterising the amount of cloud is with the octas system. It works by describing how much the of the sky is covered by cloud, out of 8. 8/8 means that the entire sky is covered in cloud.
Few 1-2 FEW
Scattered 3-4 SCT
Broken 5-7 BKN
Overcast 8 OVC
Describe the flight conditions in the presence of inversions.
Inversions have some good aspects and some not so good for VFR.
An inversion layer can trap moisture, dust and so on below it, while above it the conditions remain perfect.
If VFR is conducted at low levels there are dangers, but at higher levels inversions can be a distinct advantage.
Below the inversion layer, flight can be bumpy with some form of turbulence. Flight above the inversion layer is generally smooth.
Pilots must be aware of the possibility of fog forming with reduced visibility below inversions.
Also the possibility of carburettor icing below an inversion especially where moisture is available ie tracking along a coastline.
Inversions being associated with Wind Shear which can affect the climbing and descending profiles.
Subsidence inversion can be associated with extensive stratiform cloud together with a large anticyclone; which can cause “anticyclonic gloom” which can affect VFR flying.
Describe how stable and unstable air affect flying conditions.
Stable air with high moisture
Produces stratiform cloud or fog; bad conditions for VFR flying
Less moisture content -> cloud bases are higher -> visibility may be unsafe if associated with rain or drizzle
Unstable air
Produces cumuliform cloud – if closely spaced and shower activity is present; unsuitable for VFR flight
When less moist, cloud bases will be higher, cumulus clouds wider apart visibility should be good, light turbulence possible but conditions generally good for VFR flight
Explain how temperature, relative humidity and Dew Point values can be used to indicate differences in water content of air.
Relative Humidity and Dew Point are useful and practical indicators of the “dampness ” of air and the likelihood of cloud / fog formation and precipitation.
VFR flying can be more difficult / unsafe if the resulting cloud base is very low.
8.4.8 Identify areas of light, moderate and strong winds on a weather map.
In order to obtain the applicable weather information for your flight, first you must log on.
Once logged in, you are shown a map of the country. You must click on the the areas of the map that are applicable with your flight (the areas that you will be flying to/in)
Once the areas are selected, click on “get weather briefing” to be presented with the appropriate weather including; SIGMETS, ARFORS, TAF’s and METARS.
MetFlight’s other features also include things such as Webcams, Radar, cloud and rain forecasts as well as other charts and features than provide you with information on the prevailing weather conditions and forecasts.
Have a play around with all the features so that you are familiar with MetFlight and that you can make appropriate go or no go decisions.
How the mountain range lifts the air, cools and causes rain