Explain how illumination from the sun or moon have an effect on visibility.
Since visibility of air is related to transparency, it follows that whether it is day or night if there is no change in transparency there is no change in visibility
Illumination from the sun or moon have no influence on visibility, but are required to determine visibility range
Explain what is meant by transparency of air.
Transparency of air refers to the level of impurities
The lesser the impurities the better the transparency
Define meteorological visibility.
Visibility refers to the ability to see through air
The fewer impurities in the air the greater the visibility, thus the further we can see
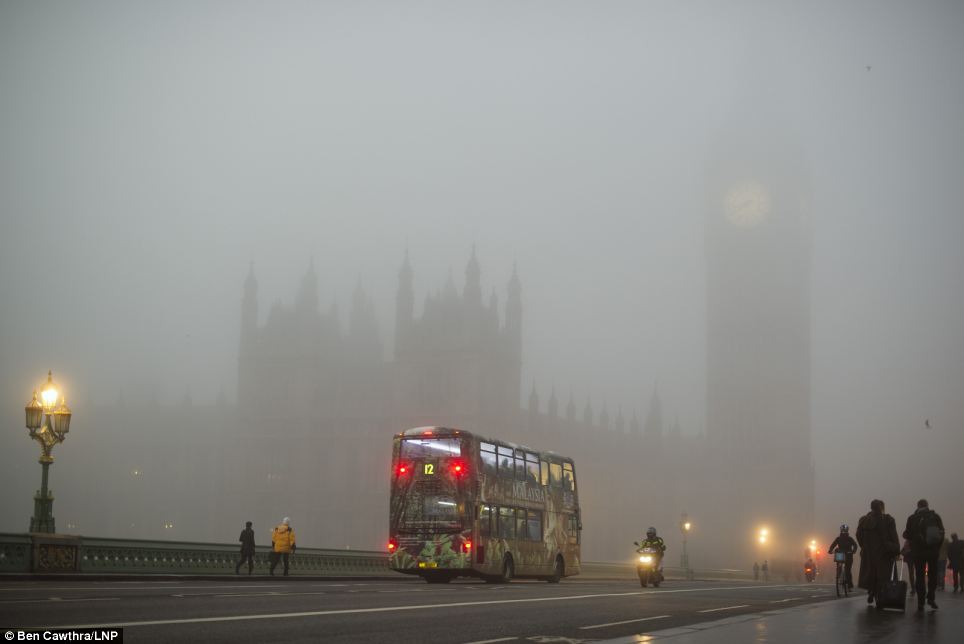

Describe the operational problems associated with fog.

There are two sets of issues
1) Departure problems
– The fog can be easily misjudged based on an apparently thin layer but within a few kilometers worse or clearer conditions may exist
– Once having taken off through fog it is unlikely that a pilot would be able to land at the same airport
– A climb out in mountainous terrain will be affected by poor visibility
2) Arrival Problems
– on approach if the fog is developing, the slant range must be considered
– danger is involved when trying to land at the end of the day – in shadow the runway can be seen at right angles but on final approach the visibility distance may not be suffiicient
.png)
.jpeg)
f) Frontal fog
This may develop when a warm front travels across the country

e) Steaming fog
this occurs where large amounts of moisture are added to the air due to evaporation from a relatively warm surface

d) Sea fog
Two types of sea fog
1) Warm stream
– forms when the moist air above it is transported over colder adjacent surfaces. It cools below Dew point and condenses
2) Cold stream
– this forms when a moist warm airflow is carried across a cold stream or a cold bay.
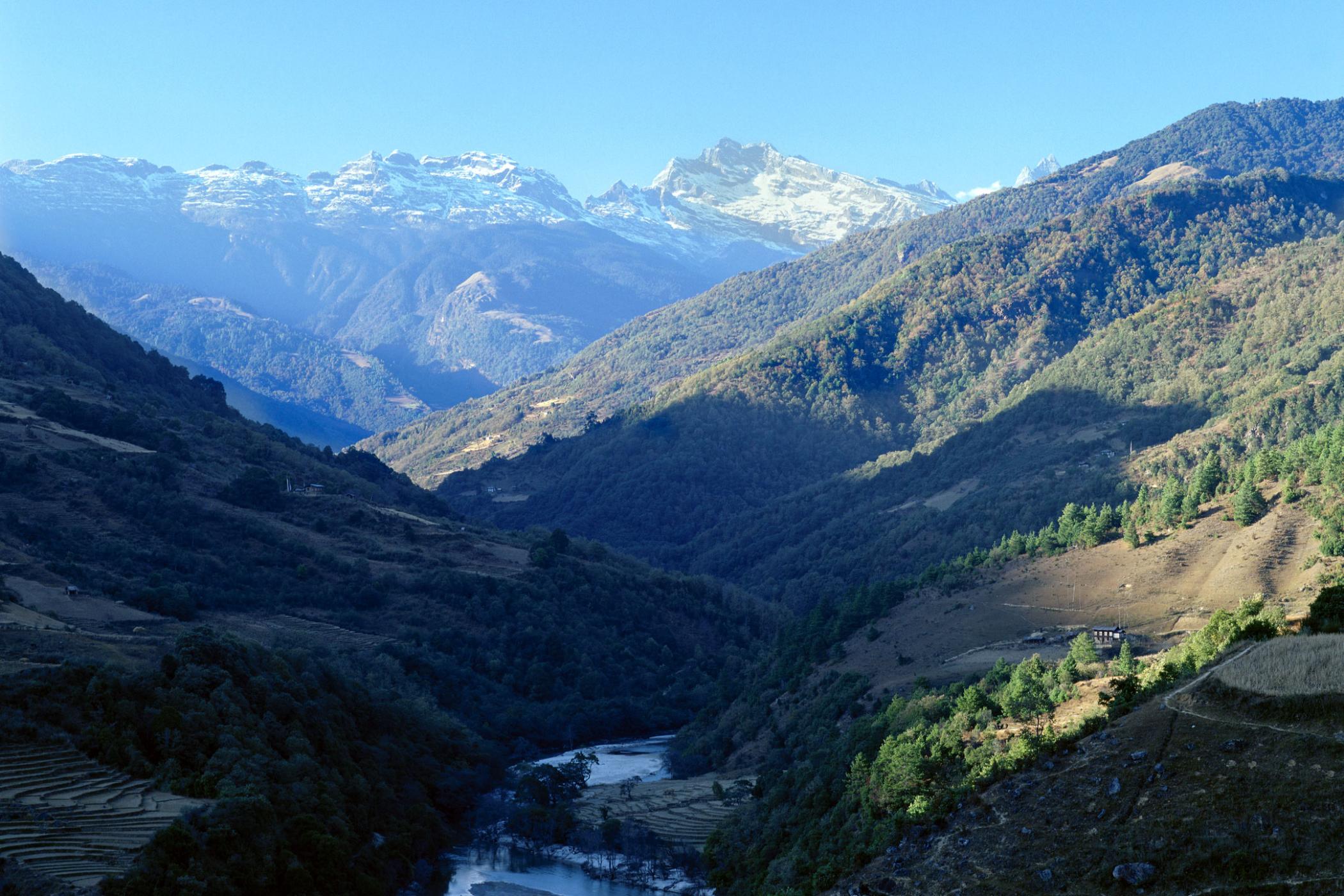

c) Valley fog
Common in mountainous terrain
Rivers and streams increase the risk of high humidity
Valley floors are cold / cooler
The cold valley walls enhance katabatic (downhill) flow causing cold air to collect

a) Radiation fog
When the surface cools in the evening, the air in contact with the surface also cools through conduction
The degree of cooling of the surface depends on how readily the ground radiation is able to escape
A clear sky and clean air content facilitate free escape of terrestrial radiation
As surface temperature decreases a stage will be reached where the surface air is cooled to Dew Point then further cooling leads to condensation.
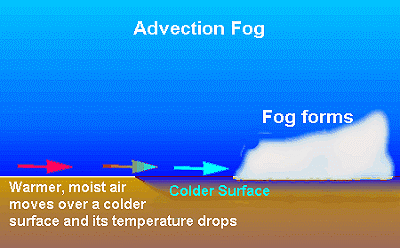
b) Advection fog
This forms when sufficiently moist air is transported over an already cold surface
Advection means horizontal transfer of air


.png)
.jpeg)




