Explain the effects on aircraft and engine performance of:
a) air density
b) air moisture content.
The mass of a molecule of water vapour is less than the mass of a molecule of dry air – in a given volume of air an increase in water content decreases the total mass.
Mass of air is proportional to its density; the greater the water content of air the less it’s density.
When the water vapour content of air increases the RH goes up and the Dew Point goes up.
Explain the effect of moisture content of air on the Dew Point.
When the water vapour content of air increases, the Relative Humidity goes up and the Dew Point goes up also. If moisture is removed the Dew Point goes down
The air temperature is always equal to or more than the Dew Point temperature
By comparing the Dew Point temperature with the air temperature we have a measure of the water content of the air
The closer the temperatures are to each other the nearer we are to saturation and then condensation occurring
Explain how the temperature of air influences its capacity to hold water vapour
Air appears to behave lie a sponge
When the air temperature increases the sponge grows and the air can hold more water vapour
When the temperature falls the sponge shrinks and the air can hold less water vapour
“The warmer the air parcel the more water vapour it can hold”
8.16.6 Define the term 'Dew Point'.
The Dew Point is the temperature at which the air becomes saturated ie the Relative Humidity reaches 100%
Dew Point temperature is the temperature to which a parcel of air must be cooled at constant pressure to become saturated
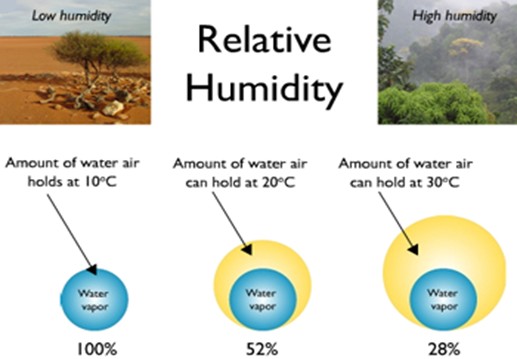
Explain the effect of changes in temperature and moisture content of air on relative humidity.
When moisture is added to the air at a given temperature, the relative humidity goes up.
When moisture content decreases relative humidity goes down.
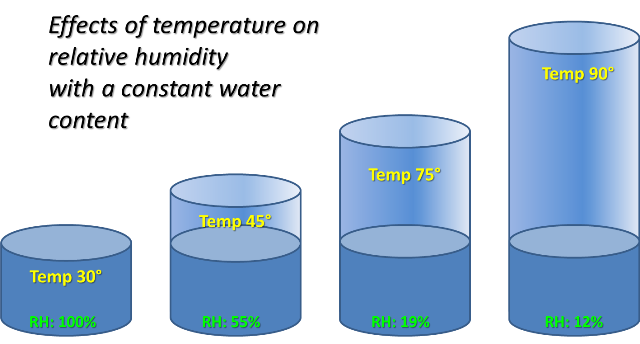
Explain what is meant by relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of water vapour present in the air.
It is the amount of water vapour the air CAN hold, expressed as a percentage.
A change in the relative humidity in the atmosphere can be casued by
– a change inb water vapour content in a parcel of air or
– a change in temperature
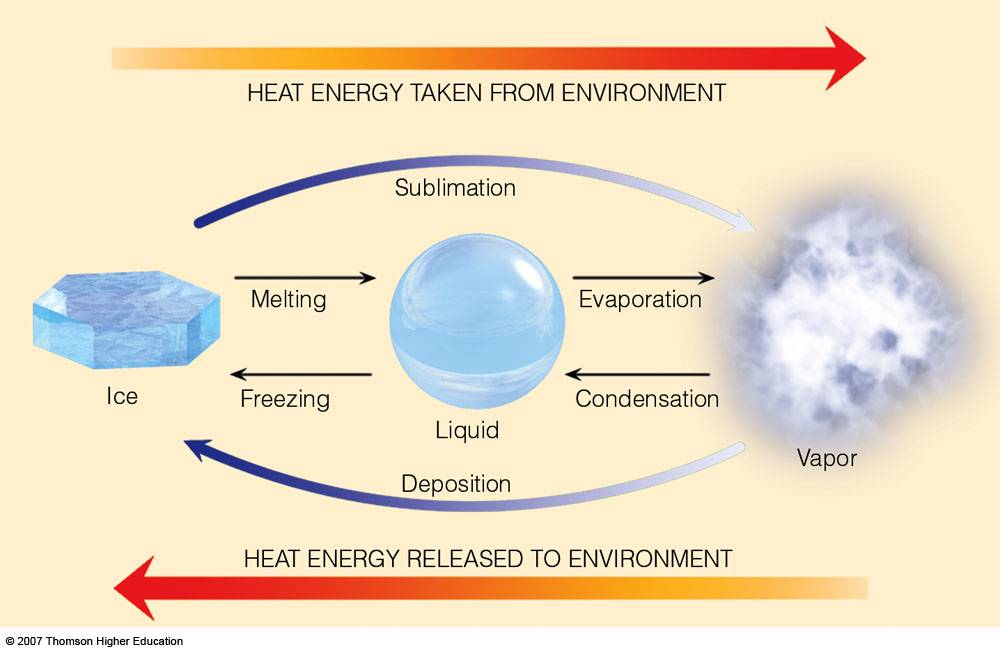
Describe the processes that change the physical state of moisture and explain how latent heat is involved in each transformation.
liquid water -> water vapour – evaporation – latent heat required
water vapour -> liquid water – condensation – latent heat released
ice -> liquid water – melting – latent heat required
ice -> water vapour – sublimation – latent heat required
liquid water -> ice – freezing – latent heat released
water vapour -> ice – deposition – latent heat released
State the effect of the following on the rate of evaporation:
a) air temperature;
b) moisture content of air;
c) atmospheric pressure;
d) the wind.
Evaporation is the change from liquid water to water vapour.
The ability of air to absorb water as a vapor depends mainly on the air temperature.
The warmer the air, the more water vapor it can hold; and the colder the air the less vapor it can hold.
The rate of evaporation will be greatest when the air is warm and dry, the pressure is low and a wind is blowing.
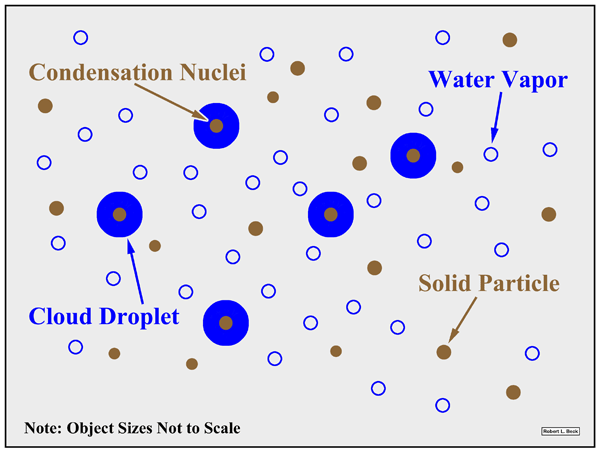
Explain the function of condensation nuclei during condensation.
The condensation process, requires the presence of condensation nuclei such as salt, carbon, soot etc around which the water vapour can cling to which creates liquid water drops.
In a dusty environment, there is more condensation compared to a clean environment which has delayed condensation.
State the significance of the reease of latent heat into the atmosphere during cloud formation
Clouds form through the process of condensation and this releases latent heat into the atmosphere
The released heat destabilises the atmosphere if enough cloud is formed and enough heat generated, it can force the atmosphere to become unstable. Now the clouds can grow unchecked turning into cumulonimbus or thunderstorm clouds



